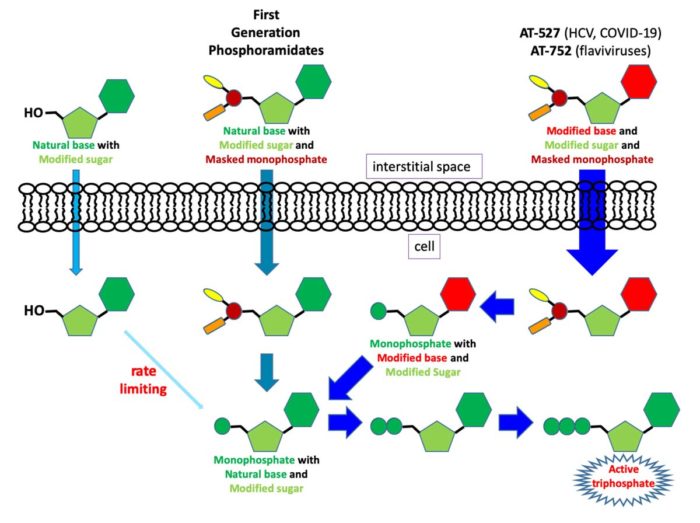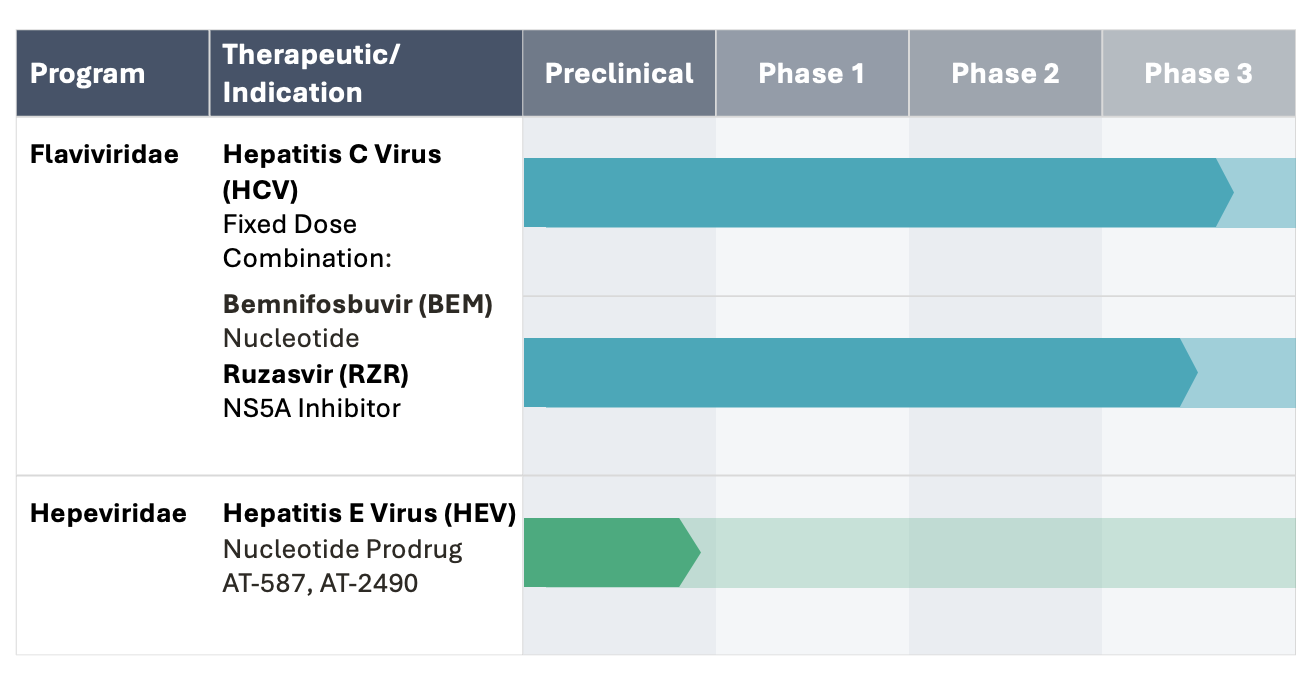
RNA Viruses
The prevalent cause of severe human viral diseases.
Single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses account for a large number of clinically serious global pathogens and are the cause of many potentially life-threatening diseases: coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, hepatitis C, dengue, RSV, yellow fever, Ebola, Zika, West Nile, and encephalitis viruses.
The activity of a key viral enzyme, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, also known as RNA polymerase, is required for replication and propagation of these viruses. The structure of this enzyme is highly conserved across RNA viruses. Most viral RNA polymerases have been identified on the basis of comparative sequence analysis, but it is important to know that viral genome replication is initiated by two different and distinct mechanisms.